What is 3rd Generation (3G) or IMT-2000?
Telecommunication system has been developping from Analog cellular to digital cellular.
Analog cellular systems are commonly referred to as first generation systems. The digital systems currently in use, such as GSM, PDC, cdmaOne (IS-95) and US-TDMA (IS-136), are second generation systems. These systems have enabled voice communications to go wireless in many of the leading markets, and customers are increasingly finding value also in other services, such as text messaging and access to data networks, which are starting to grow rapidly.
Facebook, Youtube, twitter and other social media which everyone are using to share information, to watch movies, send picture messages, game etc. so new technology was develpped called WCDMA or 3G.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) defined the key requirements for International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 (IMT-2000) services, commonly known as 3G.
3G, short for third generation, is the third generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology. It is the upgrade for 2G and 2.5G GPRS networks, for faster internet speed. This is based on a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunications use services and networks that comply with the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specifications by the International Telecommunication Union. 3G finds application in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV.
Third generation systems are designed for multimedia communication: with them person-to- person communication can be enhanced with high quality images and video, and access to information and services on public and private networks will be enhanced by the higher data rates and new flexible communication capabilities of third generation systems. This, together with the continuing evolution of the second generation systems, will create new business opportunities not only for manufacturers and operators, but also for the providers of content and applications using these networks.
WCDMA technology has emerged as the most widely adopted third generation air interface. Its specification has been created in 3GPP (the 3rd Generation Partnership Project), which is the joint standardisation project of the standardisation bodies from Europe, Japan, Korea, the USA and China. Within 3GPP, WCDMA is called UTRA (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access) FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) and TDD (Time Division Duplex), the name WCDMA being used to cover both FDD and TDD operation.
Improved system capacity, backward compatibitlity with Second Generation (2G) systems, multimedia support, and high speed packet data services meeting the following criteria:
What is Analog cellular and Digital cellular systems?
Analog cellular systems are commonly referred to as first generation systems. The digital systems currently in use, such as GSM, PDC, cdmaOne (IS-95) and US-TDMA (IS-136), are second generation systems. These systems have enabled voice communications to go wireless in many of the leading markets, and customers are increasingly finding value also in other services, such as text messaging and access to data networks, which are starting to grow rapidly.
Facebook, Youtube, twitter and other social media which everyone are using to share information, to watch movies, send picture messages, game etc. so new technology was develpped called WCDMA or 3G.
What is 3G or third generation?
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) defined the key requirements for International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 (IMT-2000) services, commonly known as 3G.
3G, short for third generation, is the third generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology. It is the upgrade for 2G and 2.5G GPRS networks, for faster internet speed. This is based on a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunications use services and networks that comply with the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specifications by the International Telecommunication Union. 3G finds application in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV.
Third generation systems are designed for multimedia communication: with them person-to- person communication can be enhanced with high quality images and video, and access to information and services on public and private networks will be enhanced by the higher data rates and new flexible communication capabilities of third generation systems. This, together with the continuing evolution of the second generation systems, will create new business opportunities not only for manufacturers and operators, but also for the providers of content and applications using these networks.
What is WCDMA technology?
WCDMA technology has emerged as the most widely adopted third generation air interface. Its specification has been created in 3GPP (the 3rd Generation Partnership Project), which is the joint standardisation project of the standardisation bodies from Europe, Japan, Korea, the USA and China. Within 3GPP, WCDMA is called UTRA (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access) FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) and TDD (Time Division Duplex), the name WCDMA being used to cover both FDD and TDD operation.
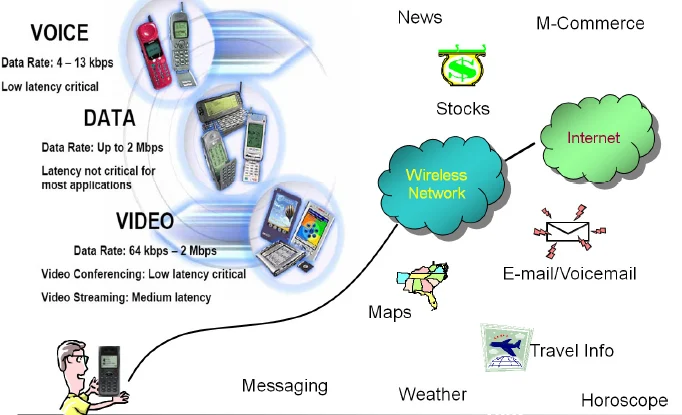 |
| WCDMA Data Services over Wireless |
Third-generation (3G) systems will support:
- High data rates: Minimum of 144 kbit/s in all radio environments ,
- 384 kbps in pedestrian or urban environments and 2 Mbit/s in low mobility and indoor environments.
- Circuit-switched and packet-switched services, such as Internet Protocol (IP) traffic and real-time video.
- Good voice quality (comparable to wire-line quality).
- Greater capacity and improved spectrum efficiency.
- Several simultaneous services to end users and terminals, for multimedia services.
- Seamless incorporation of second-generation cellular systems, to avoid discontinuity between second- and third-generation systems.
- Global, i.e. international roaming, between different IMT-2000 operational environments